Signing Transactions with Web3.js via Metamask: A Step-by-Step Guide
As a developer building blockchain-based applications, you’re likely familiar with the concept of interacting with the blockchain. However, executing transactions programmatically from within your web application can be challenging. In this article, we’ll walk you through the process of signing transactions using Web3.js and injecting Metamask functionality into your browser to facilitate secure transaction execution.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure that:
- You have a basic understanding of JavaScript, HTML, and CSS.
- You have installed Node.js and npm (the package manager for Node.js) on your system.
- You have a blockchain-based project set up, including a contract implementation and a backend server.
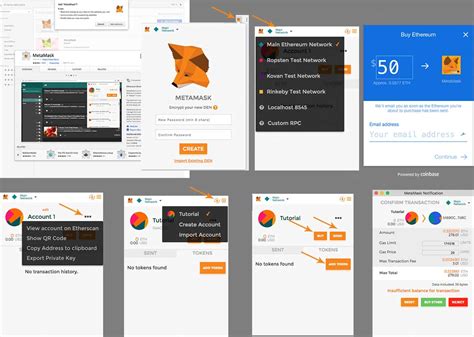
Step 1: Set up Metamask
Metamask is a browser extension that allows users to manage their digital assets, including private keys and wallet addresses. To use Metamask with Web3.js, you’ll need to:
- Install the MetaMask browser extension.
- Create an account on MetaMask by providing your email address and creating a password.
- Enable the Web3 extension in your browser settings.
Step 2: Set up Web3.js
Web3.js is a popular JavaScript library for interacting with the Ethereum blockchain. To use it, you’ll need to:
- Install Node.js and npm (as mentioned earlier).
- Create a new Node.js project using
npm init.
- Initialize your project by running
npm install web3in your terminal.
- Import Web3.js in your application:
const Web3 = require('web3').
Step 3: Inject Metamask functionality into your browser
To inject Metamask functionality into your browser, you’ll need to:
- Create a new file called
index.htmland add the following code:
Metamask Sign Transaction
Sign transaction using Metamask with Web3.js
In this code, we're using the web3.min.js file from the CDN to import Web3.js.
Step 4: Create a script.js file
Create a new file called script.js and add the following code:
const Web3 = require('web3');
const web3 = new Web3(window.ethereum);
document.getElementById('web3').addEventListener('input', (e) => {
const privateKey = e.target.value;
web3.eth accounts.add(privateKey).then((account) => {
document.getElementById('transaction-response').innerHTML = Transaction signed with account: ${account.address};
});
});
document.getElementById('sign-transaction').addEventListener('click', async () => {
try {
const signature = await web3.eth.signTransaction({
from: '0x...your_account_address...', // Replace with your account address
data: '', // Data to sign (e.g., txHash, contract methods)
gasPrice: 20, // Gas price for the transaction
});
const transactionResponse = await web3.eth.sendSignedTransaction(signature.rawTransaction);
document.getElementById('transaction-response').innerHTML = Transaction signed and sent to blockchain!;
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
});
In this code, we're using Web3.js to create a new Ethereum account using the user's private key.


Geef een reactie